Narrative or Traditional literature reviews critique and summarise a body of literature about the thesis topic. The literature is researched from the relevant databases and is generally very selective in the material used. The criteria for literature selection for a narrative review is not always made open to the reader.
These reviews are very useful in gathering and synthesising the literature located. Where a narrative approach differs from a systematic approach is in the notation of search methods criteria for selection,this can leave narrative reviews open to suggestions of bias. A literature review is an overview of the previously published works on a specific topic. The term can refer to a full scholarly paper or a section of a scholarly work such as a book, or an article. Either way, a literature review is supposed to provide the researcher/author and the audiences with a general image of the existing knowledge on the topic under question.
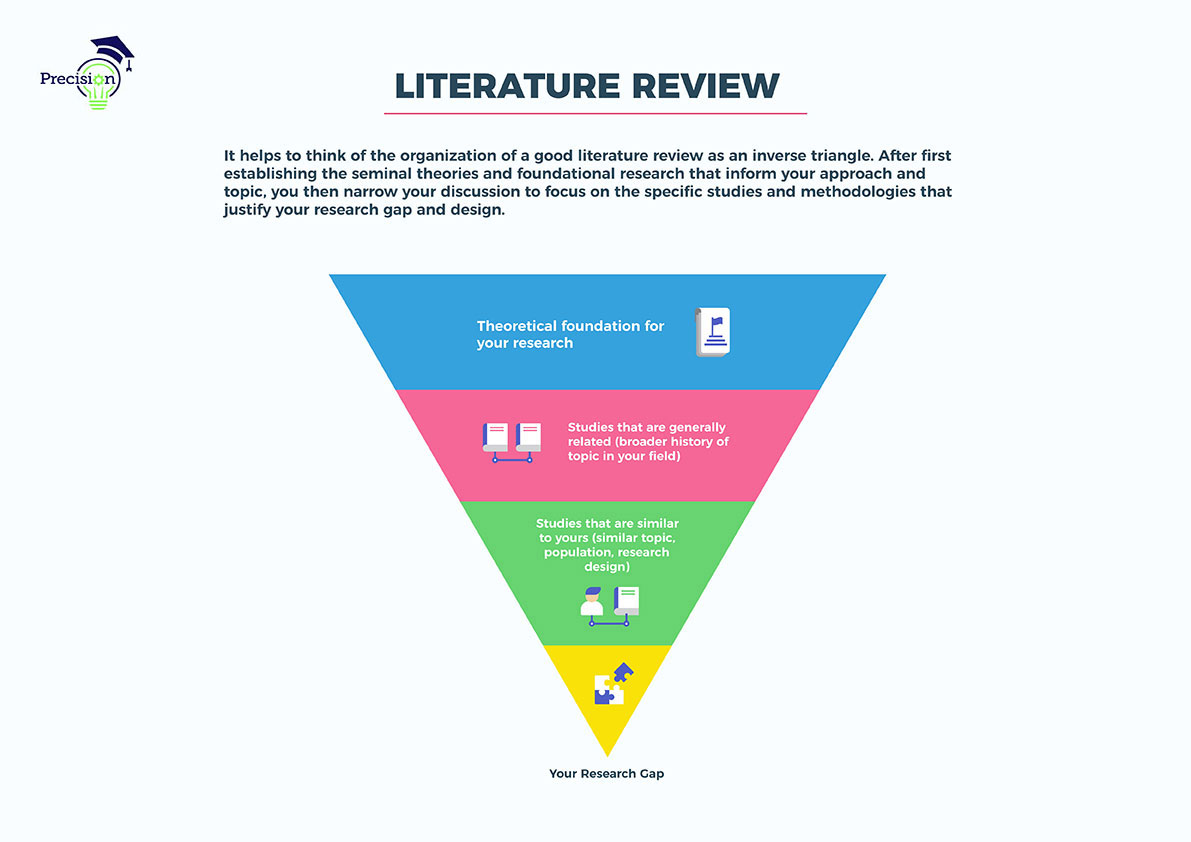
A good literature review can ensure that a proper research question has been asked and a proper theoretical framework and/or research methodology have been chosen. To be precise, a literature review serves to situate the current study within the body of the relevant literature and to provide context for the reader. In such case, the review usually precedes the methodology and results sections of the work. Literature reviews can have different types of audiences, so consider why and for whom you are writing your review.
For example, a lot of literature reviews are written as a chapter for a thesis or dissertation, so the audience will want to know in what way your research is important and original. Highlighting the gap in knowledge which your research aims to fill is particularly important in this instance because you need to convince the reader that there is an opening in the area of study. A literature review in a proposal will similarly try to convince the audience of the significance and worthiness of the proposed project.
In contrast, when you are writing a literature review for a course, your professor may want you to show that you understand what research has been done, giving you a base of knowledge. In this case, you may not need to focus as much on proving where the gaps in knowledge lie, but rather, that you know what the major areas of study and key ideas are. A literature review summarizes and synthesizes the existing scholarly research on a particular topic.
Literature reviews are a form of academic writing commonly used in the sciences, social sciences, and humanities. However, unlike research papers, which establish new arguments and make original contributions, literature reviews organize and present existing research. As a student or academic, you might produce a literature review as a standalone paper or as a portion of a larger research project. Literature refers to a collection of published information/materials on a particular area of research or topic, such as books and journal articles of academic value.
However, your literature review does not need to be inclusive of every article and book that has been written on your topic because that will be too broad. Rather, it should include the key sources related to the main debates, trends and gaps in your research area. You've decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales.
This is because you've just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale's portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980's. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. In addition, this type of literature review is usually much longer than the literature review introducing a study.
At the end of the review is a conclusion that once again explicitly ties all of these works together to show how this analysis is itself a contribution to the literature. While it is not necessary to include the terms "Literature Review" or "Review of the Literature" in the title, many literature reviews do indicate the type of article in their title. Whether or not that is necessary or appropriate can also depend on the specific author instructions of the target journal. Have a look at this article for more input on how to compile a stand-alone review article that is insightful and helpful for other researchers in your field. In a larger piece of written work, such as a dissertation or project, a literature review is usually one of the first tasks carried out after deciding on a topic. Reading combined with critical analysis can help to refine a topic and frame research questions.
A literature review establishes familiarity with and understanding of current research in a particular field before carrying out a new investigation. Conducting a literature review should enable you to find out what research has already been done and identify what is unknown within your topic. Literature reviews exist within different types of scholarly works with varying foci and emphases. Short or miniature literature reviews can be presented in journal articles, book chapters, or coursework assignments to set the background for the research work and provide a general understanding of the research topic. Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic.
If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper's investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Beyond looking at the research findings obtained in academia, an assessment of the policies and practices implemented by the authorities and industry was undertaken. Pay particular attention to the author's concluding chapter and/or afterword. List the principal topics, and briefly summarize the author's ideas about these topics, main points, and conclusions. If appropriate and to help clarify your overall evaluation, use specific references to text and quotations to support your statements. If your thesis has been well argued, the conclusion should follow naturally.
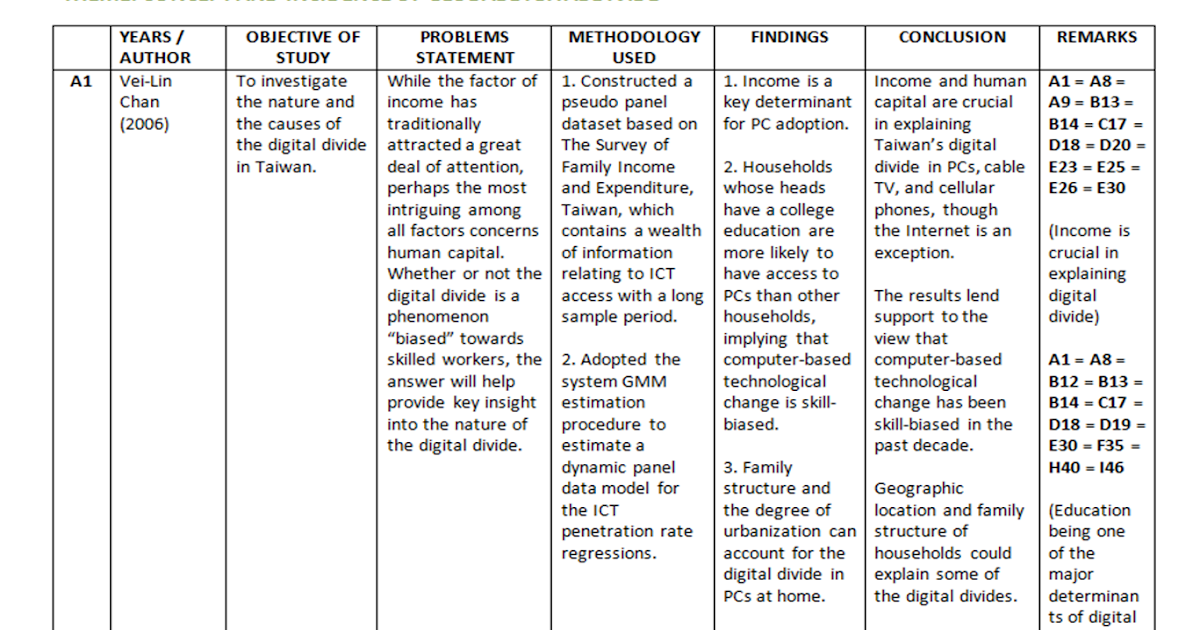
If you've compared the book to any other works or used other sources in writing the review, be sure to cite them at the end of your book review in the same writing style as your bibliographic heading of the book. Many researchers struggle when it comes to writing literature review for their research paper. A literature review is a comprehensive overview of all the knowledge available on a specific topic till date. Literature review is one of the pillars on which your research idea stands since it provides context, relevance, and background to the research problem you are exploring. A systematic literature review identifies, selects and critically appraises research in order to answer a clearly formulated question (Dewey, A. & Drahota, A. 2016).
The systematic review should follow a clearly defined protocol or plan where the criteria is clearly stated before the review is conducted. It is a comprehensive, transparent search conducted over multiple databases and grey literature that can be replicated and reproduced by other researchers. It involves planning a well thought out search strategy which has a specific focus or answers a defined question. The review identifies the type of information searched, critiqued and reported within known timeframes. The search terms, search strategies and limits all need to be included in the review. Your hypothesis, argument, or guiding concept is the "golden thread" that will ultimately tie the works together and provide readers with specific insights they didn't have before reading your literature review.
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word "review" in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read are also excellent entry points into your own research. A meta-analysis is typically a systematic review using statistical methods to effectively combine the data used on all selected studies to produce a more reliable result.
Unlike some of the other well-known "reviews" (e.g. theater or book reviews), literature reviews steer clear of opinion statements. Instead, they summarize and critically assess a body of scholarly literature from a relatively objective perspective. Writing a literature review is a rigorous process, requiring a thorough evaluation of the quality and findings of each source discussed. The purpose of a literature review is to provide a review of writings on the given topic in order to establish the reviewer's own position in the existing field of scholarship on that topic.
A literature review provides a reader with a comprehensive look at previous discussions prior to the one the reviewer will be making in his/her own research paper, thesis, or dissertation. In short, a literature review shows readers where the reviewer is entering the academic conversation on a particular topic in the context of existing scholarship. However, there are three common mistakes that researchers make when including literature reviews in the discussion section. First, they mention all sorts of studies, some of which are not even relevant to the topic under investigation. Second, instead of citing the original article, they cite a related article that mentions the original article.
Lastly, some authors cite previous work solely based on the abstract, without even going through the entire paper. Literature reviews constantly feed new research, that constantly feeds literature reviews…and we could go on and on. The fact is, one acts like a force over the other and this is what makes science, as a global discipline, constantly develop and evolve. As a scientist, writing a literature review can be very beneficial to your career, and set you apart from the expert elite in your field of interest. But it also can be an overwhelming task, so don't hesitate in contacting Elsevier for text editing services, either for profound edition or just a last revision. You can also save time by letting us suggest and make the necessary amendments to your manuscript, so that it fits the structural pattern of a literature review.
Who knows how many worldwide researchers you will impact with your next perfectly written literature review. Finally, after you have finished drafting your literature review, be sure toreceive proofreading and language editing for your academic work. A competent proofread who understands academic writing conventions and the specific style guides used by academic journals will ensure that your paper is ready for publication in your target journal. The more reviews one reads in the context of an article, the better one understands the specific demands for literature in a given study.
The literature review found at the beginning of a journal article is used to introduce research related to the specific study and is found in the Introduction section, usually near the end. It is shorter than a stand-alone review because it must limit its scope to very specific studies and theories that are directly relevant to this study. Its purpose is to set research precedence and provide support for the study's theory, methods, results, and/or conclusions. Not all research articles contain an explicit review of the literature, but many do, whether it is a discrete section or indistinguishable from the rest of the Introduction. The two types of literature reviews commonly found in journals are those introducing research articles and stand-alone literature analyses. Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible.
In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not. A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic.
It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. An annotated bibliography is a list of your references with a summary of the content and the publication's relationship to your research question. A literature review is an overview of the topic, an explanation of how publications differ from one another, and an examination of how each publication contributes to the discussion and understanding of the topic.
Acknowledgements -- scholarly studies in the social sciences often take many years to write, so authors frequently acknowledge the help and support of others in getting their research published. This can be as innocuous as acknowledging the author's family or the publisher. However, an author may acknowledge prominent scholars or subject experts, staff at key research centers, people who curate important archival collections, or organizations that funded the research.
In these particular cases, it may be worth noting these sources of support in your review, particularly if the funding organization is biased or its mission is to promote a particular agenda. A literature review is a survey and discussion of the literature in a given area of study. It is a concise overview of what has been studied, argued, and established about a topic, and it is usually organized chronologically or thematically.
It is not an annotated bibliography, because it groups related works together and discusses trends and developments rather than focusing on one item at a time. It is not a summary; rather, it evaluates previous and current research in regard to how relevant and/or useful it is and how it relates to your own research. This section differs slightly between reviews which are part of research articles and narrative reviews. The section describes the main conclusions from analysis of all the current studies and puts forth further avenues for research.
This section requires critical interpretation by the author such that the review adds value to existing literature. It should bring out ideas/hypotheses that can explain any discrepancies and provide solutions to existing problems. Sometimes referred to as a systematic literature review or meta-analysis, this type is a critical survey that attempts to "evaluate and interpret all available research evidence relevant to a particular question" . In essence, a literature review identifies, evaluates and synthesises the relevant literature within a particular field of research. It illuminates how knowledge has evolved within the field, highlighting what has already been done, what is generally accepted, what is emerging and what is the current state of thinking on the topic.
In addition, within research-based texts such as a Doctoral thesis, a literature review identifies a research gap (i.e. unexplored or under-researched areas) and articulates how a particular research project addresses this gap. These literature reviews are generally a bit broader in scope and can extend further back in time. This means that sometimes a scientific literature review can be highly theoretical, in addition to focusing on specific methods and outcomes of previous studies. In addition, all of its sections refer to the literature rather than detailing a current study. A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time.
As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? A literature review is a piece of academic writing demonstrating knowledge and understanding of the academic literature on a specific topic placed in context. A literature review also includes a critical evaluation of the material; this is why it is called a literature review rather than a literature report. A degree in English language and literature is designed to get you reading books, analyzing theories, critiquing prose and verse, and taking a more critical look at the signs and words surrounding us every day. The aim is to get students thinking creatively and analytically about the English language; this differs from other modern language degrees as it is intended for students already proficient in written and spoken English.
AnEnglish degree canfocus equally on the literature and language sides, while others specialize in one or the other; this will usually be clear from the course title. There are several different paths for careers in literature as a graduate. You can also take graduate courses and become a teacher, lecturer, or journalist, with common crossovers for graduating English students including business, law, and education. Or you can use your analytical skills to move into unexpected careers such as marketing, advertising, or pretty much anything you are willing you adapt to. There are also obvious positions available in the publishing industry, from editor, to proofreader, to literary agent. A literature review assignment is a critical analysis of previous research about a specific topic.
This is different from a literature review for a research project, where you use past research findings to identify and justify your new research topic. A literature review is a study – or, more accurately, a survey – involving scholarly material, with the aim to discuss published information about a specific topic or research question. Therefore, to write a literature review, it is compulsory that you are a real expert in the object of study. The results and findings will be published and made available to the public, namely scientists working in the same area of research. The "literature" of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. "Literature" could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL.























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.